The times of manual routing techniques and being attached to a landline are long gone. Now, there are advanced possibilities of person-to-person communication, voice and video calls, and instant messaging.

This article explores how evolving technology, such as SIP-based solutions, can contribute to companies' efficiency and improved customer experience. Additionally, it will not neglect important drawbacks in terms of its security.
What Is SIP Telephony?
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is a signaling protocol that is used to manage multimedia communications, such as voice and video calls. Additionally, it is used to facilitate other applications like instant messaging and data transmission.

SIP initiates, maintains, modifies, and terminates real-time sessions over two or more endpoints. Meaning, it enables the connection between multiple people to transmit information between them. It became a major structural component in IP telephony, not least because SIP is an open standard.
How Does It Work?
The SIP Protocol has a readable text-based format for displaying information, similar to HTTP. It uses a simple request/response mechanism that makes troubleshooting easier, i.e., identifying issues in the flow of the system. It receives requests from clients and responses from servers.
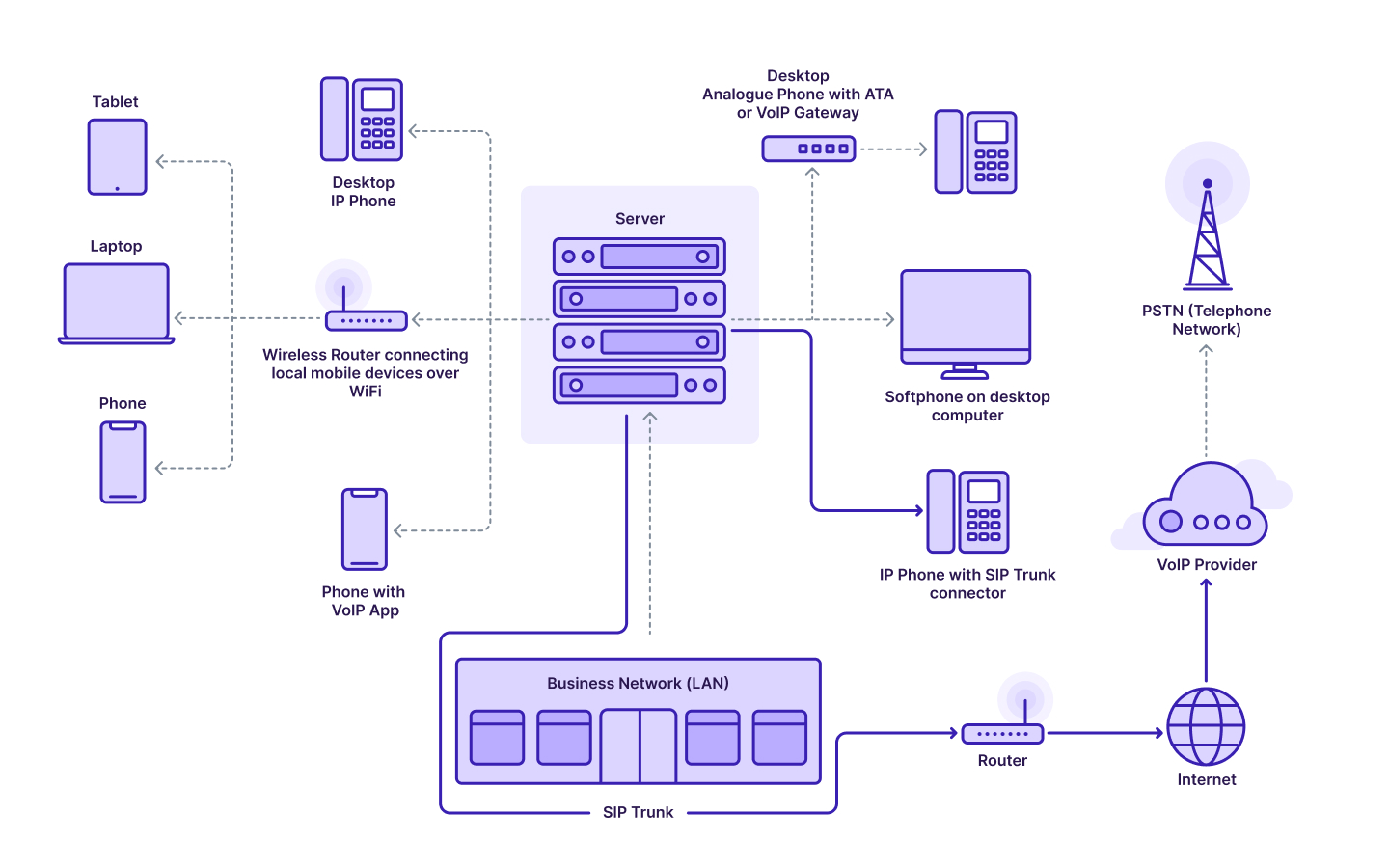
SIP will also work with other protocols, namely SDP (Session Description Protocol). SIP messages contain an SDP declaration that defines which is prepared to accept the data, the media type for a user to receive, the port number for the incoming media, and other information for a given session.

There are minimal requirements to deploy SIP: stable Internet connection and an IP or VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) telephony. You can install the system to a phone with a special adapter, a computer, or a smartphone. In any case, it will not be much trouble.
A machine SIP phone looks like a regular phone but connects to the data network through a mini-hub. Alternatively, a program-based SIP phone is installed directly to your computer or smartphone (the last one via an app).
Key Differences Between SIP and VoIP
The terms SIP and VoIP are closely connected but are not interchangeable. VoIP is a type of hardware/software that enables calls over internal networks or the Internet. SIP is a protocol for managing VoIP calls. Here are some distinct differences:
- Scope – VoIP is an umbrella term for the family of technologies Internet Protocol to transport voice information. SIP is used within these technologies;
- Forms of media – SIP supports a wider list of mediums than VoIP, which only transmits audio data;
- Devices – SIP doesn’t necessarily require a computer to function, whereas VoIP needs to be connected to a computer;
- Traffic handling – SIP has a peer-to-peer style system, and VoIP processes everything from a central network.
Benefits of SIP Technology in Business
From an operational and financial standpoint, there are significant benefits in switching to SIP telephony. Business can consider it as a replacement to ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network, i.e., traditional lines) since SIP telephony:
- Minimizes the costs for national, international and to mobile calls;
- Offers global reach with no additional investments;
- Combines all communications into the same network;
- Increases mobility since you do not depend on physical infrastructure;
- Scales up or down depending on your business requirements;
- Provides the versatility of use and easy manipulation;
- Serves as a perfect enabler for adopting UC strategies.
SIP Security Issues
With such a promising future in terms of replacing traditional telephone services, SIP needs to provide overall confidence in the quality and security level of the system. To make a real impact for the users, it should not only match that of existing landlines but improve on it.

Like HTML, a SIP message can contain malware and infect your computer. For example, SIP users can become victims of an IoT-like attack. The planted malware can use command-and-control-servers to access data on your computer and execute cyberattacks like DDoS and phishing.
The SIP systems use TLS (Transport Layer Security) to hide the communication between devices from inspection and interference. Also, the SIP telephony utilizes the S/MIME encryption standard for email authentication, message integrity, and non-repudiation of origin. But even though these measures make the system more secure, they are not flawless.
Conclusion
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) builds on the IP communications foundation that transports and delivers content over multiple devices and platforms. The SIP protocol enables calling sessions and requires only a reliable Internet connection. It gives businesses a competitive advantage by cutting costs and simplifying phone system operations.
Even though there are security issues inherent to wireless environments, there are ways to manage them. Some vulnerabilities can be mitigated if you treat your SIP network just like web traffic, for instance, by applying data encryption. Overall, SIP telephony demonstrates obvious advantages but requires diligent attention not to become compromised.