A virtual agent is an AI-based software program that communicates through voice or text. A virtual agent is also known as an intelligent virtual agent (IVA), virtual rep, or virtual chat agent.
Companies commonly integrate virtual agents into their customer support service on apps or on websites to respond to standard requests or handle simple issues. For instance, banking virtual agents often help customers find their nearest ATM.
Virtual agents are also used to cover employee needs. Companies can deploy virtual agents within an IT department, for example, to provide help desk-type services such as resetting computer passwords. Agents can also guide staff through routine tasks or processes. One of the most widespread types of virtual agents is a chatbot that can understand and respond via email, messaging, or voice.
Virtual agents are very similar to virtual assistants that use artificial intelligence to understand natural language voice commands and perform tasks. You are probably familiar with virtual assistants like Apple’s Siri and Amazon’s Alexa.
Differences between Virtual Agents and Virtual Assistants
At a glance, the terms “virtual agent” and “virtual assistant” look similar; however, they serve people in various capacities and differ in their usage purpose and complexity.
Virtual assistants can perform Internet research and a wide range of digital tasks such as playing music, turning on a TV, or creating a meeting reminder in response to a user's request. Commonly, virtual assistants can handle a broader variety of interaction than virtual agents and can be deployed on a smartphone app or on a device such as a smart speaker.
On the other hand, virtual agents are commonly used in corporate infrastructure to cover customer or employee needs. Currently, 23% of customer service organizations use AI chatbots.*
Virtual agents are often optimized to deal with a specific environment or situation. In case of complex issues, virtual agents may reroute tasks to a human agent if needed.
The term “virtual agent” can also refer to a human being that works as a remote assistant.
How it Works
Firstly, companies identify areas and workflows that don’t require a live person. In the case of a call center, companies often automate the process of answering frequently asked questions.
When the areas and workflows are determined, companies create scripts using visual editors such as Voximplant Kit. The editor can only recognize individual words as responses, so this only works well if a question can have a single response.
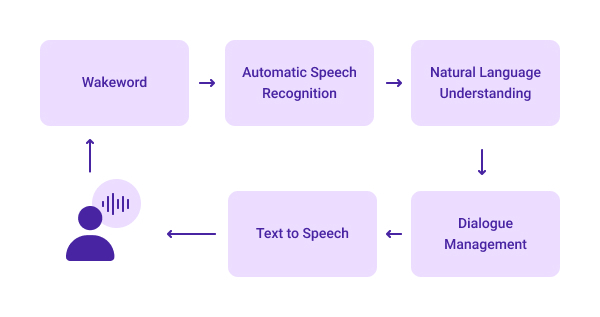
Virtual agents need to be trained to work correctly without sacrificing the user experience. Chatbots use conversational AI capabilities such as Automatic Speech Recognition, Natural Language Processing (NLP), Dialog Management, and Machine Learning (ML) to comprehend and carry on a conversation.
- Speech Recognition converts customer speech to text and prepares data for further analysis
- Natural Language Processing provides language analysis that helps agents interpret what users are looking for
- Dialog Management is responsible for the selection of actions and responses to user requests and other input data
- Machine Learning focuses on resolving issues and allows virtual agents to improve the responses and interactions they have
Virtual agent platforms can be connected to the company’s database to provide more personalized and accurate responses based on customer purchase history. In addition, the AI capabilities built into these platforms allow virtual agents to ‘learn’ so that they can become more efficient and cope with a wider range of tasks.
NLU systems like Dialogflow understand intents and know if you provided partial information through its interface and ML training.
Say the system asks, what is your address? If the user answers "New York" Kit's ASR's won't be able to determine if the user should have also included their street name.
Dialogflow knows enough to follow-up and ask “What is your address,” “what is your ZIP code,” etc.
Virtual Agent Use Cases
Virtual agents are appropriate for both internal and client facing departments of a company. Below are three examples of how agents can be used.
Customer Service
Virtual agents can assist customers during their journey through the sales funnel. Agents can provide product consultation, cancel transactions, or even trigger the refund process. This frees the operator’s time to focus on more complicated tasks. If an agent cannot handle a task on its own, the conversation will be routed to an operator.
Machine learning has the ability to study a customer’s behavior and consider his/her purchase history to personalize the conversation. With this technology, virtual agents can even provide product recommendations or suggestions.
Service Desks
Virtual agents are also used to reduce the ticket volume of IT service desks and support employees.
Let’s imagine that your employee has an issue with his computer audio. An agent can be pre-trained to ask if an employee uses headphones or speakers. Depending on the answer, the agent can then provide a suggestion for troubleshooting. If the employee responds that the headphones are broken, the agent can automatically send a request for new headphones without calling the service desk.
Customer Research
To improve the customer experience, you can create a survey scenario and gather feedback from customers speaking different languages. Virtual agent platforms cover different languages and dialects and allow companies to survey multiple customers simultaneously.
Voximplant Kit, for instance, provides survey templates to allow you to automatically conduct a phone survey with more than 20 languages in just five minutes.
Using a Virtual Agent
Companies interested in integrating virtual agents into their workflow through a cloud-based provider or software vendors will have to train a robot. This process can take weeks to months depending on the desired level of confidence.
Virtual agents can only use information that was uploaded into the AI system. If the data is irrelevant, customers will receive false information. Thus, this stage of data preparation is particularly important since it affects the robot’s efficiency in dealing with your customers.
Virtual agents are powered by machine learning technology, which is constantly improving over time while the system gains more data and self-learns.
To speed up the initial stage, virtual agent platforms pre-train their robots for customer service tasks. For instance, IBM Watson trains virtual agents to understand typical customer service requests in various ways. Watson’s agents also don’t require any installation.
Capabilities
Virtual agents have several advanced capabilities that can lower your business costs and enhance the user experience.
- Omnichannel access: Enables varied access to agents including websites, messaging platforms, mobile, or web apps.
- Conversational interface: Natural language understanding technology allows robots to understand users even if they don’t use technical jargon or specific terminology.
- Intelligent responses: With machine learning, agents can maintain an accurate and relevant conversation flow and improve customer retention.
- Automation features: Not all providers pre-train agents for processing automated requests. Automation speeds up the development process and reduces human involvement.
- Software integration: Connecting agents with ITSM tools and customer databases such as a CRM makes it easyto share data between apps.
Conclusion
Virtual agents automate communications between customers and businesses, reducing the volume of calls, emails, and chat sessions that a human operator would need to manually process.
At the same time, building proper scripts and integrating agents with a CRM system guarantee the accuracy of responses. This makes agents a useful tool for marketing, sales, and customer support purposes.
Agents have already become a vital part of various business industries. Currently, virtual agents can only handle standard tasks, but in the future they will be able to perform more complicated tasks and impact a business strategy.
*According to the Salesforce survey