Android: ConnectionService
A self-managed ConnectionService handles multiple calls from various applications that utilize the ConnectionService API, such as switching between calls on hold or answering an incoming call while already on one. Additionally, it enables answering or declining calls on wearable devices.
Manifest declarations and permissions
To integrate a self-managed ConnectionService, declare the MANAGE_OWN_CALLS permission in the AndroidManifest.xml file.
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.MANAGE_OWN_CALLS" />
To connect Telecom to ConnectionService, declare the service itself and the BIND_TELECOM_CONNECTION_SERVICE permission in the AndroidManifest.xml file.
<service
android:name=".services.CallConnectionService"
android:permission="android.permission.BIND_TELECOM_CONNECTION_SERVICE">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.telecom.ConnectionService" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
TelecomManager and PhoneAccount
TelecomManager uses a registered PhoneAccount to place a phone/VoIP call. To build a PhoneAccount, the app should provide a valid PhoneAccountHandle which refers to the connection service implementation that Telecom uses to interact with the app.
A PhoneAccountHandle consists of a component name of the associated connection service and a string identifier that is unique among PhoneAccountHandles with the same component name. See PhoneAccountHandler on the Android Developers site.
For a self-managed ConnectionService, set PhoneAccount.CAPABILITY_SELF_MANAGED to indicate that this PhoneAccount is responsible for managing its own Connection.
Create and manage a call connection
Android Telecom Connection
A Connection represents a phone call or connection to a remote endpoint that carries voice and/or video traffic.
This definition necessitates the creation of a new Android Telecom Connection for each outgoing (before ICall.start()) and incoming (before ICall.answer()) Voximplant call. This ensures that the Voximplant ICall interface manages a VoIP call, and the Telecom Connection registers this call within the telecom subsystem.
Every self-managed Connection should be specified with the following parameters:
You can also utilize additional features, such as placing a call on hold or muting it, using the connectionCapabilities. For a comprehensive list of features, refer to the Android Developers site.
Please note that each new Connection should be passed to the Voximplant SDK via IAudioDeviceManager.setTelecomConnection() to manage audio devices.
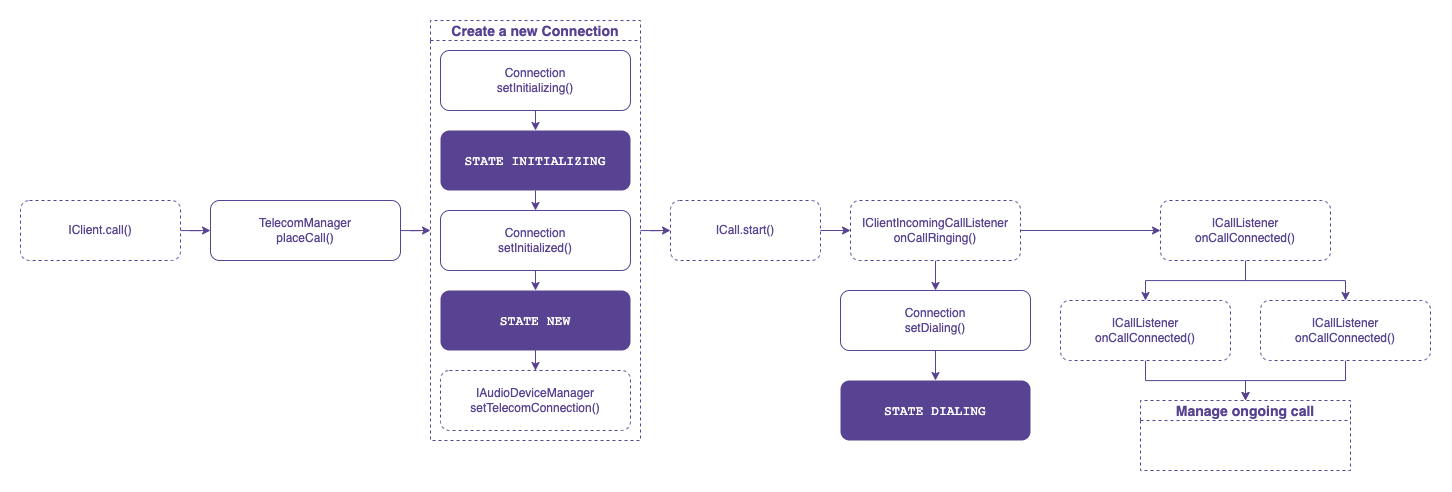
Make an outgoing call
To initiate an outgoing call, ensure that a PhoneAccount is registered and then utilize the TelecomManager.placeCall() method.
A self-managed ConnectionService should contain EXTRA_PHONE_ACCOUNT_HANDLE in the Bundle extra to specify the PhoneAccountHandle associated with it.
If the app can place an outgoing call, the telecom subsystem calls the onCreateOutgoingConnection() method where the app should return a new Connection to represent a new outgoing call.
It is important to call Connection.setActive() once the outgoing call is connected. It notifies the telecom subsystem that the call is in progress.
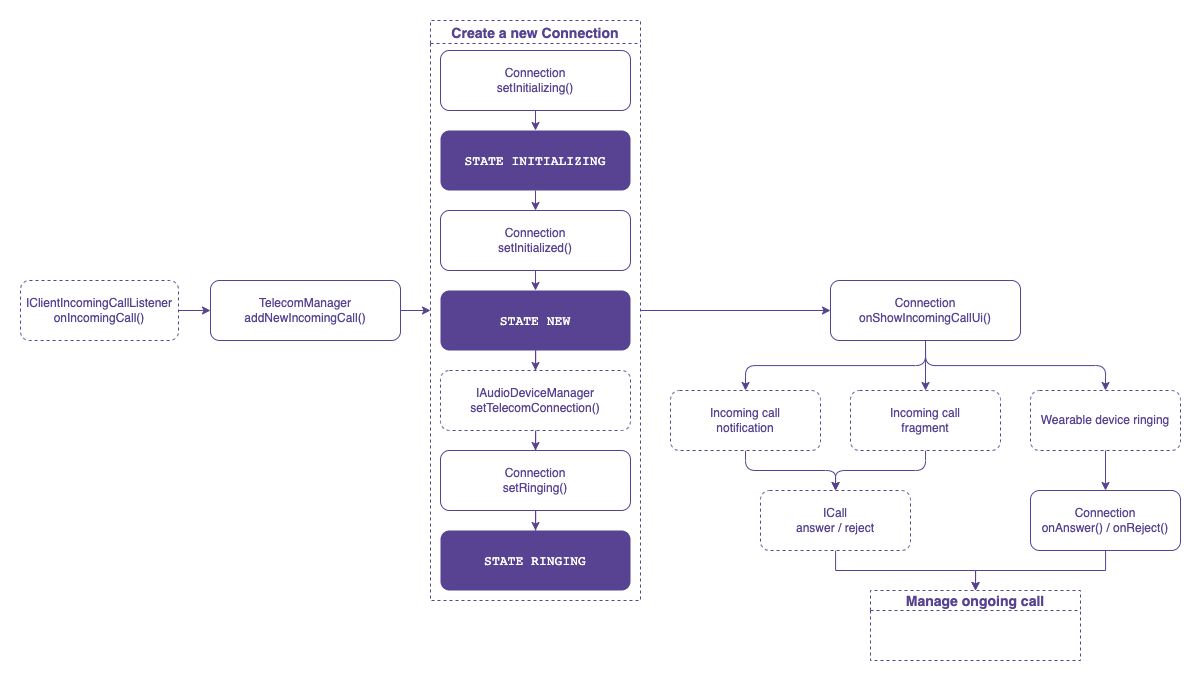
Receive an incoming call
When the app receives an incoming call via the Voximplant SDK (IClientIncomingCallListener.onIncomingCall()), it is necessary to check the PhoneAccount registration in the system. To register a new incoming call, use the TelecomManager.addNewIncomingCall() method.
The telecom subsystem binds to the app's ConnectionService and requests a new Connection instance for the incoming call via the ConnectionService.onCreateIncomingConnection() API. Upon receiving this event, the application needs to create a Connection.
For a self-managed connection service, the Connection triggers the Connection.onShowIncomingCallUi() event to let the application know when to display the incoming call UI. Showing a notification with full-screen intent is recommended.
The user may accept and reject the incoming call from the incoming call notification or wearable devices:
If the user answers or rejects the call from the notification, it should be handled by the application via PendingIntent.
If the user answers or rejects the call from a wearable device, the Connection informs you about this action by triggering the
Connection.onAnswer()orConnection.onReject()event.
To answer the call, you need the ICall.answer() API. Establish the call connection via the Voximplant Android SDK and update the Connection state to active once the call is connected (ICallListener.onCallConnected()).
To reject the call, you need the ICall.reject() API. The Voximplant Android SDK triggers the ICallListener.onCallDisconnected() event as soon as the call is ended. The application should set the Connection status to disconnected and destroy the Connection.
Manage ongoing call
The Voximplant Android SDK offers the following capabilities for ongoing calls:
Put the call on hold
Mute
Change the audio device
The Voximplant Android SDK fully manages the mute and audio device changing capabilities, eliminating the need for any Connection API call.
To put the call on hold, the application’s Connection state should be changed using the Connection.setOnHold() API. However, ensure that ICall.hold() is completed successfully before changing the Connection state.
1) On devices running Android API level 28 or higher, when an incoming PSTN call is answered by the user, the VoIP ongoing call is put on hold by TelecomManager and can be resumed after the PSTN call ends. On devices running Android API level 27 or lower, only one app can maintain an ongoing call at any given time. This constraint means that the ongoing call is terminated.
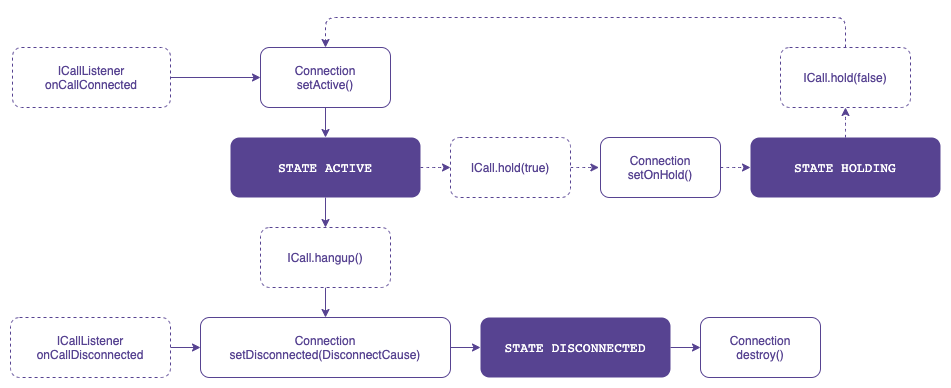
End ongoing call
Either a user or a remote party can end an ongoing call.
If the user ends the call, the application should call the ICall.hangup() API, so the Voximplant Android SDK triggers the ICallListener.onCallDisconnected() event.
If the remote party ends the call, the Voximplant Android SDK informs the application by triggering the ICallListener.onCallDisconnected() event.
After receiving the ICallListener.onCallDisconnected() event, you need to:
- Change the Connection status to disconnected via the
Connection.setDisconnected(DisconnectCause)API. - Destroy the Connection via the
Connection.destroy()API to destroy the Connection object.
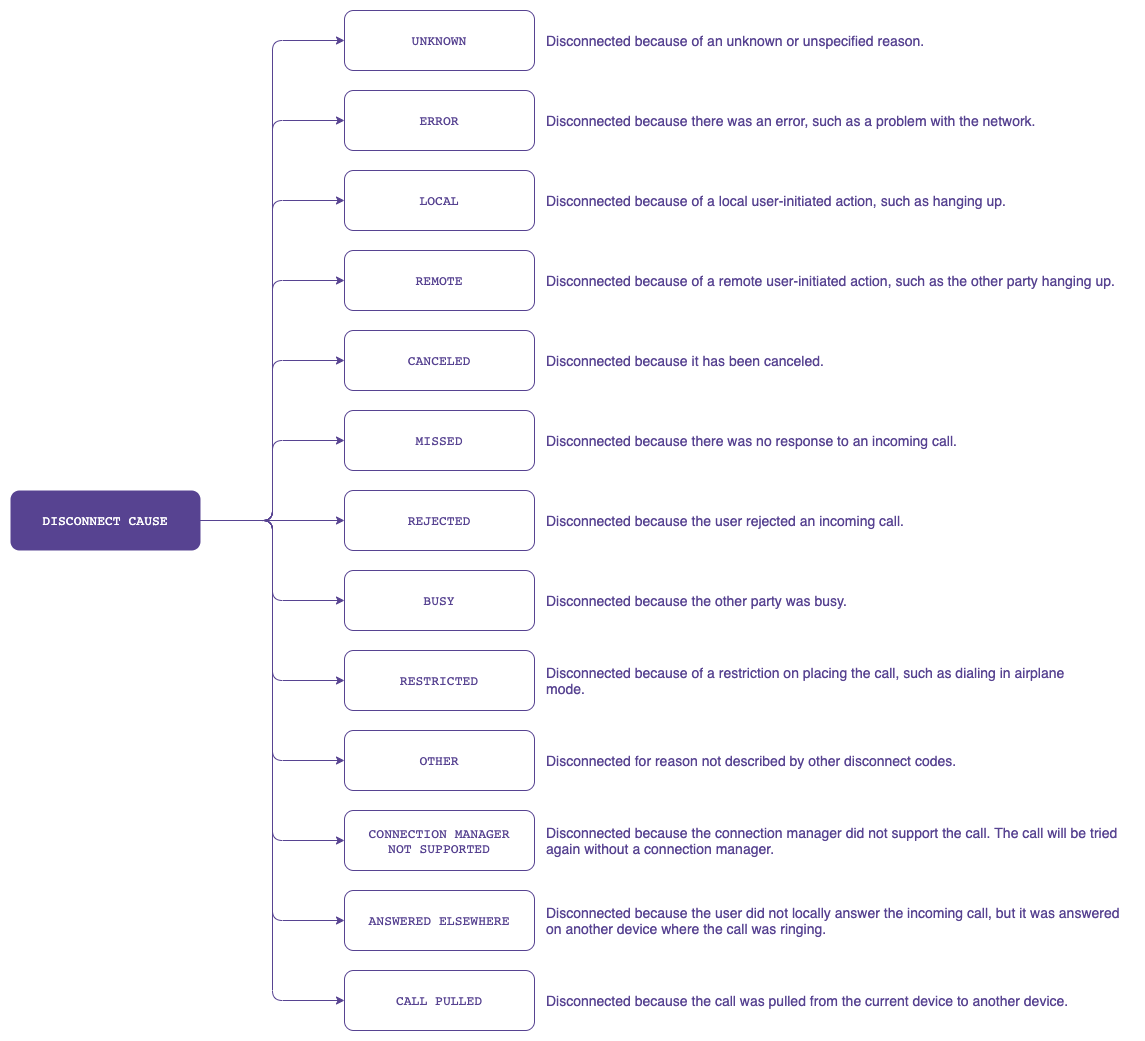
DisconnectCause describes the cause of a disconnected call. It always includes a code describing the generic cause of the disconnect. Optionally, it may include a label and/or description to be displayed to the user. The ConnectionService provides localized versions of the label and description. It may also contain a disconnect reason used for the logs, and not intended for the user.
See DisconnectCause on the Android Developers site for more information.